This article offers an in-depth examination of the elbow joint, its structure, function, and clinical relevance, providing a foundation for both academic study and practical application.
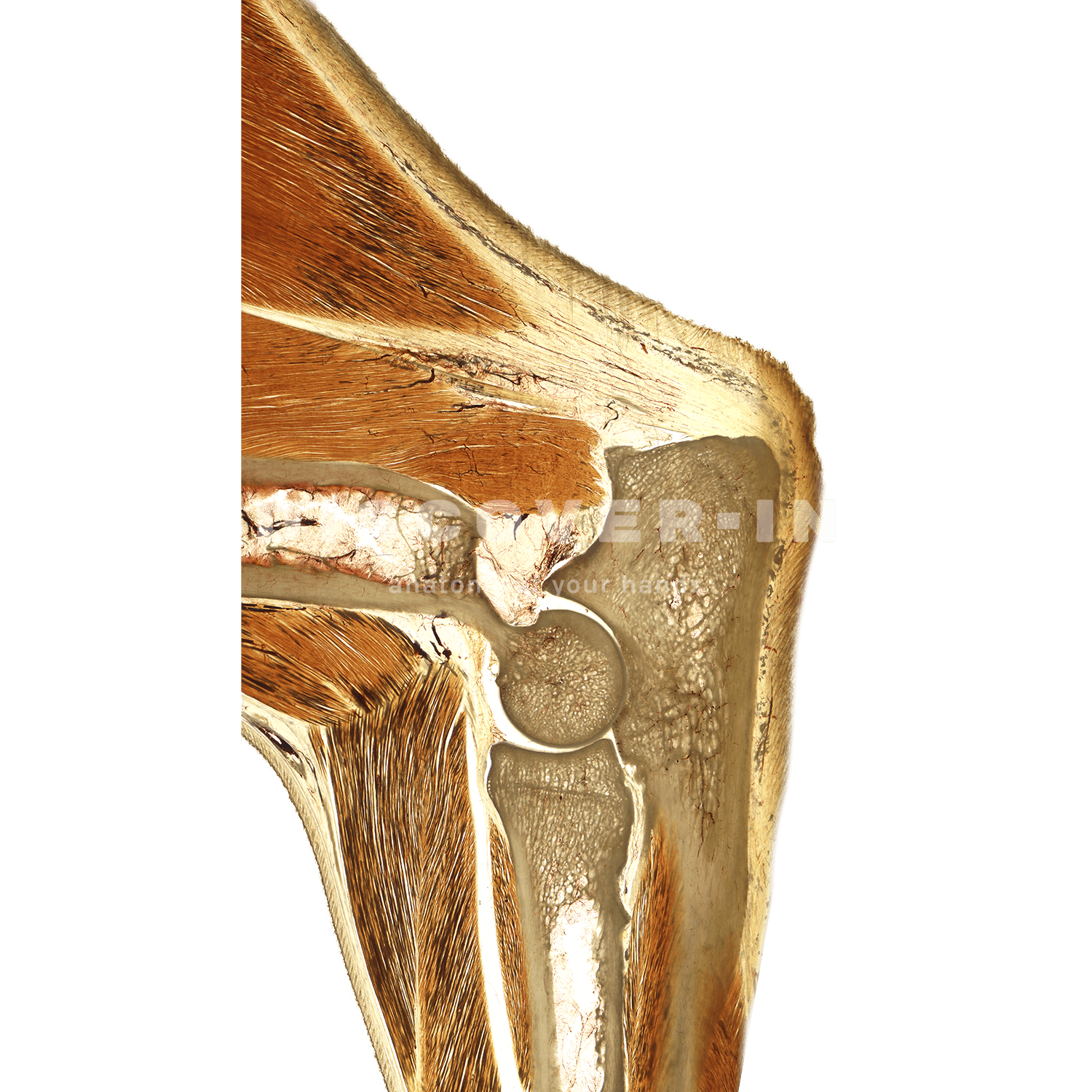
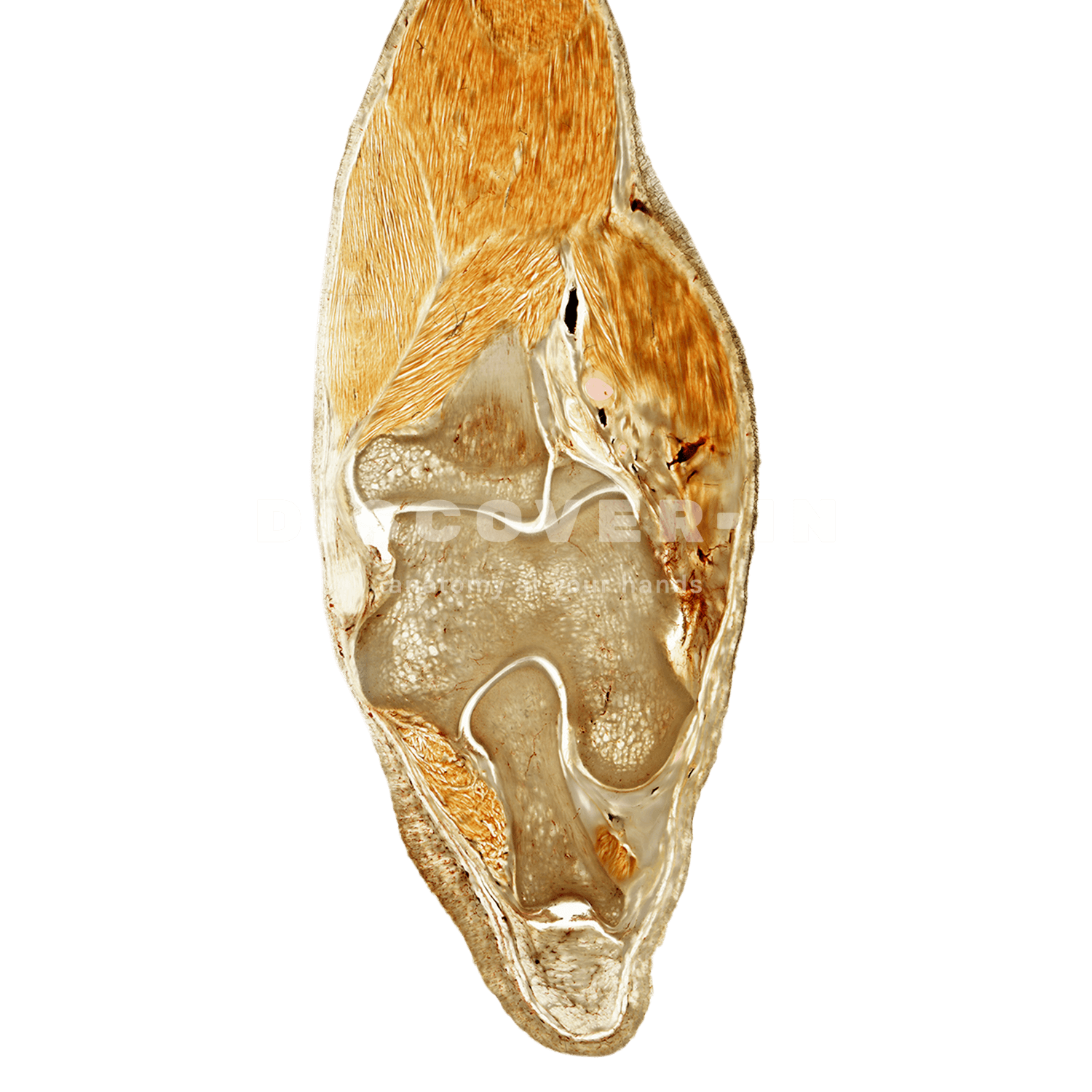
The canine elbow is a highly complex synovial joint that plays a pivotal role in locomotion and weight-bearing. Through anatomical dissection and detailed study, we can uncover the biomechanical intricacies of this joint, shedding light on normal function as well as common pathological conditions. This exploration serves as a valuable resource for improving diagnosis, treatment, and overall canine care.
The Structure of the Canine Elbow
The canine elbow is composed of three main bones: the humerus, radius, and ulna. These bones come together to form a hinge joint that allows for flexion and extension of the front leg. Additionally, the elbow joint is supported by a network of ligaments and tendons that help stabilize the joint during movement.
Canine Elbow Dissection
Dissecting the canine elbow allows us to examine the joint’s internal structures in detail. By carefully dissecting each component, we can gain a better understanding of how the elbow functions and what can cause dysfunction or disease.
The ligaments and tendons in the canine elbow play a crucial role in supporting the joint and facilitating smooth movement. These structures can be damaged by trauma or wear and tear, leading to conditions such as elbow dysplasia or ligament tears.
Early recognition of abnormalities within the elbow joint is vital for effective intervention and long-term management. Diagnostic techniques such as radiography, computed tomography (CT), and arthroscopy have significantly enhanced our ability to assess joint integrity and detect subtle pathological changes. Combined with a solid anatomical understanding gained through dissection, these tools empower veterinarians to make accurate diagnoses, develop targeted treatment plans, and ultimately improve the quality of life for canine patients.